The four pieces are pieces of ring, put them so that the mirrors form an entire ring.
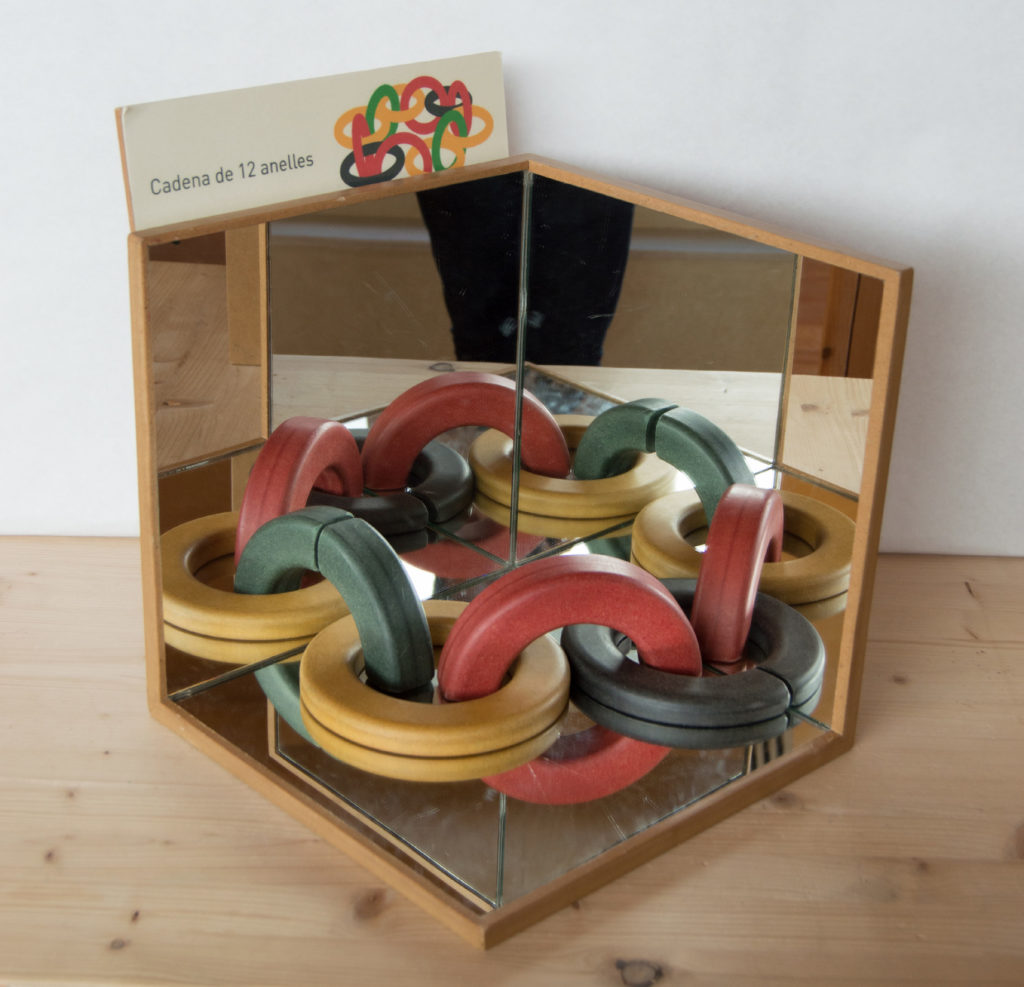
Link the rings so that a closed chain of 12 rings is visible.
The 3 perpendicular mirrors
As you know, with a mirror we duplicate the images of the objects we put in it.
With a second mirror we double the images again. How many images do we see, therefore, of the objects in front of us using two mirrors? Check your answer, you need to see 4 images.
And with a third mirror perpendicular to the previous ones, the images are duplicated again. Thus, this arrangement of 3 perpendicular mirrors (orthogonal) multiplies by 8. Check that you can count 8 images of any object you put on it.
A little fractions
The yellow piece is half of a complete ring, cut along, when placed inside it is multiplied by 8:
\frac{1}{2} anella groga * 8 = 4 anelles grogues
The red piece is half of a complete ring, cut through, when placed inside it is multiplied by 8:
\frac{1}{2} anella vermella * 8 = 4 anelles vermella
The blue piece is a quarter of a ring
\frac{1}{4} anella blava * 8 = 2 anelles blaves
The blue piece is a quarter of a ring
\frac{1}{4} anella negra * 8 = 2 anelles negres
En total 4 + 4 + 2 + 2 = 12 anelles
- Hotel Area: Sala Emma Castelnuovo
- Minimum age: from 6 years old.
- Required time: 5 minutes.
- Number of participants: One or more people
- Keywords: mirror, reflection, fractions
- Taxonomy: Geometry


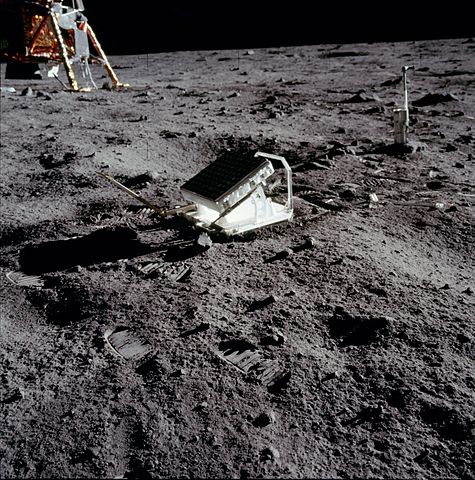
Practical applications: from bicycles to the Moon
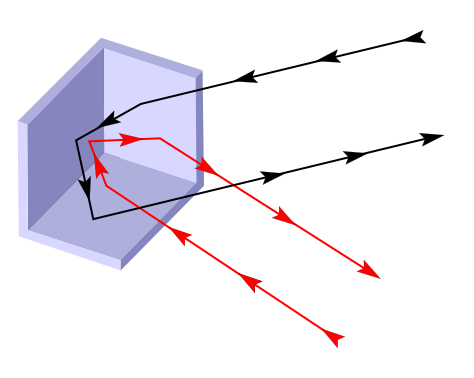
This arrangement of 3 perpendicular mirrors has a peculiarity that makes it very useful:
It reflects the rays in the same direction they have arrived. As the image illustrates, the light rays come in the direction that comes, after 3 reflections one in each of the mirrors, returns to the direction of incidence.
You can check this: look at your image at the junction point of the three mirrors, tilt your head and check that you are still seeing it.
The reflectors of the vehicles, are made by a set of small orthogonal mirrors, in this way they return the light they receive, for example from the headlights of another vehicle, in the same direction of arrival that in this way sees reflected their own lights, whatever their position.

The Apollo (USA) and Lunik (USSR) explorations on the Moon from 1969 to 1973 left several reflectors on its surface.
Measuring the return time of a laser beam sent from Earth allows you to know very accurately the distance to the Moon at a certain time.
In this way we know that the Moon moves away from the Earth 3.8 cm each year due to the tides of the Earth.

